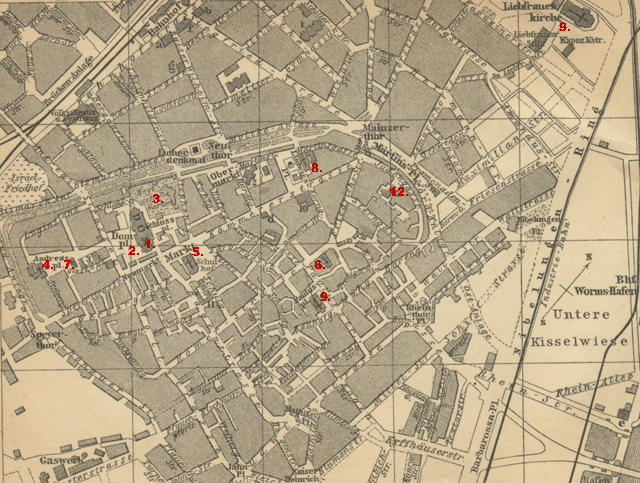
1. Dom, 2. Johanneskirche (no longer standing), 3. Heyl Musuem, 4. Andreaskirche, 5. Driefaltigkeirskerche, 6. Friedrichskirche, 7. Magnuskirche, 8. Martinskirche, 9. Pauluskirche, 9. too. Liebfrauenkirche, 12. Synagog
|
Worms, Rhineland, Germany - Old Images GOEHLE INTRODUCTION - Peter Goehle, Senior - Wallreuther - Kieser |
|
Worms - A
Bit of History Worms has been inhabited since the time of the Celts in the stone age. The city was under the control of the Germanic tribes when they were incorporated into the Roman Empire. The Roman forum stood at the present site of the Dom of St. Peter. After the fall of the Roman Empire the city was ruled by various Germanic tribes. Under the Franks the city became Christian and Worms became a center of the Holy Roman Empire. It was the seat of both the Emperor and the Bishop. In 1521 Martin Luther was was condemned by the Edict of Worms decreed by the Emperor Charles V. The Emperor abandoned Worms when plague ravaged the city in the sixteenth century. The city walls were destroyed during the Thirty Years War (1618-1648). In the War of the League of Augsburg (1688-1697) Louis XIV again destroyed the city. Still further horrors occurred under the Napoleonic occupation when over 20 churches were sold, and the Bishops residence, the cathedral and other churches were used as stables and hay barns.
WORMSGoehle and Related Families in Worms Peter Goehle was born in 1852 in Hernsheim, Hessen-Darmstadt, a town just outside the city of Worms. See Peter Goehle Peter Goehle's g g g grandmother, Anne Amelia Kieser born circa 1691 the daughter of Bernard Kieser was most likely born in Worms. She married Johann Christopher Wallreuther in Worms in 1710. See Kieser Johann Christopher Wallreuther's half brother, Johann Anton Wallreuther, was the Roman Catholic Auxiliary Bishop of Worms from 1731 until his death in 1734. An Auxiliary Bishop is an addition bishop assigned to a see when the actual bishop for one reason or another is unable to preform all of his required functions. In this case, the bishop was also a prince who spent time at court. See Johann Anton Wallreuther at Wallreuther
Several members of the Wallreuther family were Roman Catholic priests in Worms. See Wallreuther
The Roman Catholic Churches of Worms
|

| |
| Map collection of Maggie Land Blanck
1. Dom, 2. Johanneskirche (no longer standing), 3. Heyl Musuem, 4. Andreaskirche, 5. Driefaltigkeirskerche, 6. Friedrichskirche, 7. Magnuskirche, 8. Martinskirche, 9. Pauluskirche, 9. too. Liebfrauenkirche, 12. Synagog | |
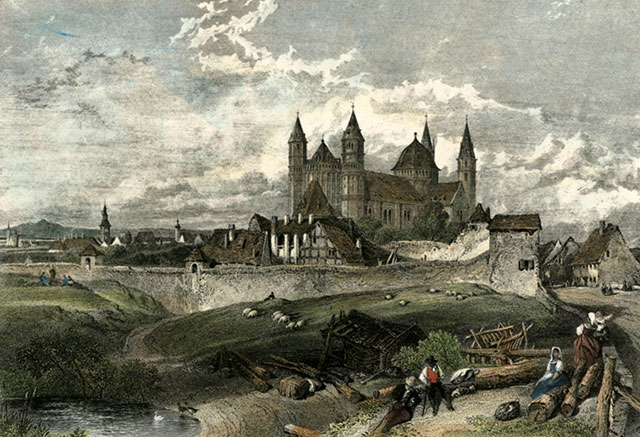
| |
| Collection of Maggie Land Blanck, 2013
Worms - an 1850 engraving after a drawing by the English artist, Myles Birket Foster (1825-1899)
| |

|
Worms a. Rh Total Postmarked 1911 |
| Collection of Maggie Land Blanck | |
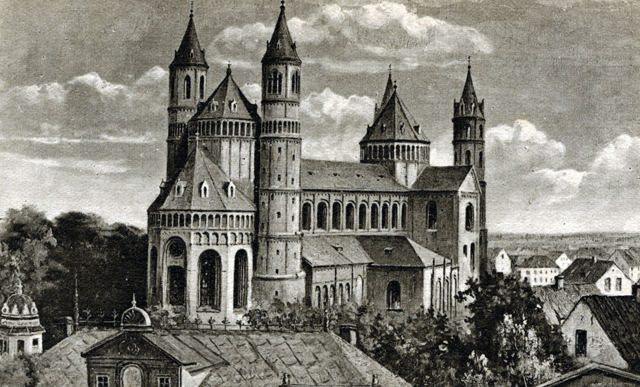
| Dom, St Peter The Dom (or Cathedral) of St Peter was the seat of the Prince-Bishop of Worms. This Romanesque church was originally consecrated in 1110. The church was extensively renovated in 1171-1192. Additions were made in the 13th century. In this church at the Imperial Diet in 1521 Martin Luther was ordered to recant his heretical theses. The Emperor Charles V presided over the assembly and as a result the Edict of Worms was degreed. "For this reason we forbid anyone from this time forward to dare, either by words or by deeds, to receive, defend, sustain, or favor the said Martin Luther. On the contrary, we want him to be apprehended and punished as a notorious heretic, as he deserves, to be brought personally before us, or to be securely guarded until those who have captured him inform us, whereupon we will order the appropriate manner of proceeding against the said Luther. Those who will help in his capture will be rewarded generously for their good work."Personal note: As a kid I always loved the "Diet of Worms". The Dom was also the site of papal election of 1048 and the Concordat of Worms in 1122.
|
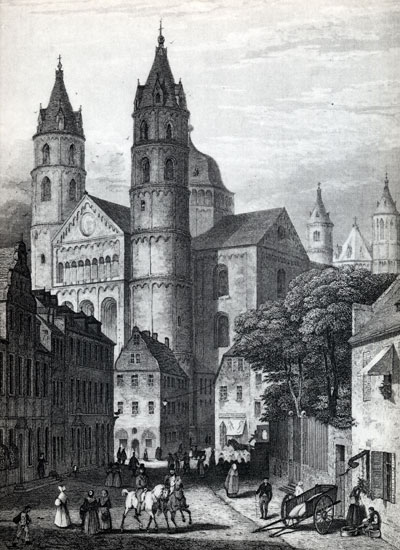
|
Der Dom Su Worms . Um 1835
Worms Cathedral (Dom) is one of the outstanding examples of
Romanesque architecture in Germany. Much of the building dates to the
11th and 12th centuries with some parts dating to the 10th century. There are some
later Gothic addidtions. See St Peter's Cathedral (Worms Cathedral)
|
| Print collection of Maggie Land Blanck, reproduction | |

| Worms a. Rh Dom v Luden. Not posted |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck | |

| Worms, Hagenstrasse - Blick auf den Dom [View of the "Dom"] |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck
| |

| Worms am Rhein Dom Not posted |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck | |
| |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011
The west choir of the Dom.
| |

| Worms am Rhein Dom/Westchor Not posted |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck | |
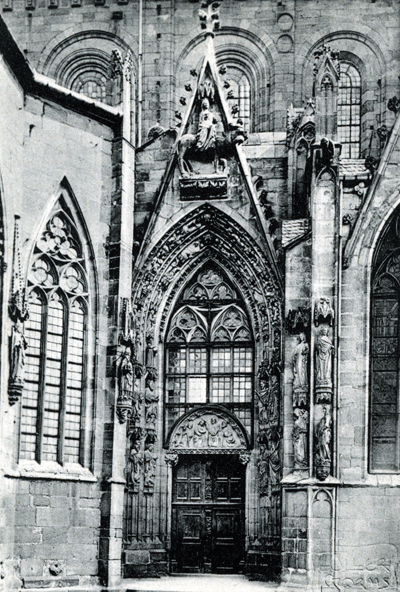
| Sudportal am Dom zu Worms [South Door of the Cathedral at Worms] |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011 | |
| Johanneskirche, St John the Baptist Johanneskirche (St John the Baptist) was the parish church of the cathedral. It was located to the west of the facade of the Dom. The building was of great antiquity, perhaps even originating in pagan times. Das Baptisterium (S. Johanniskirche) zu Worms was a three storied octagon. It was demolished in the early 1800s. Johann Anton Wallreuther (born 1673 in Kiedrich the son of Johann Matthias Wallreuther) was a priest and later Auxiliary bishop of Worms. From 1705 until 1714 J. Anton Wallreuther kept the baptismal, marriage and death records that are listed by LDS as being from Johanneskirche. He signed each record J A Wallreuther. Anno 1705 Ego Joes Antonius Wallreuther --: Theologia _ientiutus caonicus ad -- M--nian virg-men [several words I cannot read] Bapth(page turned) administrandam [several more words I cannot read].Note: It is his hanrdwriting and it is hard to read. From 1716 there are BMDs relating to Bernard Kieser (born c 1688) the son of Bernard Kieser and the brother of Anna Amelia Kieser who married Johann Christopher Wallreuther (born 1686) and the half brother of the bishop J. Anton Wallreuther. The records for Johanneskirche from 1692 to 1798 are on LDS microfilm 0996677 Items 2 and 3.
Das Baptisterium (S. Johanniskirche) zu Worms was a three storied octagon. To see a computer generated model of the Dom and the Baptistry of St John (Johanniskirche) go to Architectura Virtualis Dom Zu Worms See Wallreuther | |
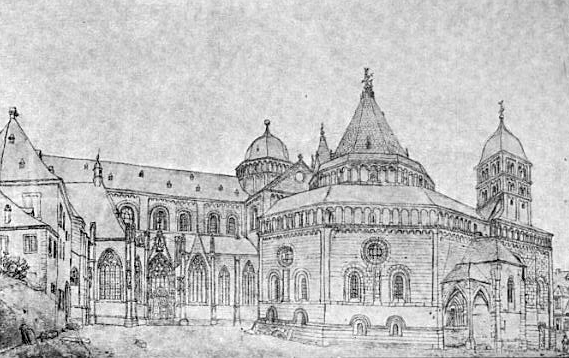
| |
| Google Book, Harvard Library, Verschwundene Wormser
Bauten: Beiträge zur Baugeschichte und
Topographie der ... By Eugen Kranzbühler, September 2011
Johanneskirche with the Dom in the background.
| |
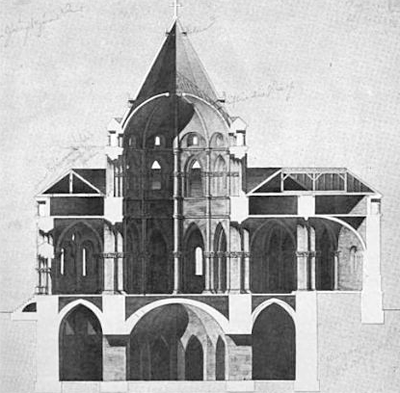
| |
| Google Book, Harvard Library, Verschwundene Wormser
Bauten: Beiträge zur Baugeschichte und
Topographie der ... By Eugen Kranzbühler, September 2011
Johanneskirche
| |
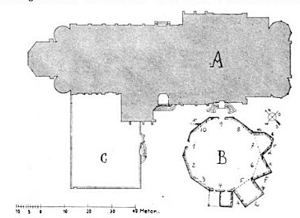
| |
| Google Book, Harvard Library, Verschwundene Wormser
Bauten: Beiträge zur Baugeschichte und
Topographie der ... By Eugen Kranzbühler, September 2011
A. Dom, B. Johanneskirche, C. Domkreuzgang und Kapitelhaus (Dom cloister and chapter house)
| |
| Markplatz
| |

| |
Collection of Maggie Land Blanck, 2013
Beyond the busy market-place looms the Cathedral of Worms, the ancient town where Luther made the vigorous defense of his doctrines | |

| Worms, Markplatz With the Dom in the background. Dated 1919. |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011
| |

| Worms, Markplatz With the Dom in the background. Dated 1919. |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011
| |

|
WORMS am Rhein - Siegfriedbrunnen Siegfried was the hero of the Nibelungen saga - the story of the royal family who settled Worms. |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011
| |

| Worms, Markplatz Posted 1903 |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck
The church is the Drifaltigkeitskirche (Trinity)
| |
| Dreifaltigkeitskirche The church of the Trinity: Dreifaltigkeitskirche (Trinity Church), Worms | |

| |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011
Worms Dreifaltigkeitskirche u Cornelianum (Trinity)
| |

| |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck
Heyl's Hof, Worms The Heylshof museum contains a collection of sculptures, porcelain and glass. Heylshof | |
| Martinskirche, St Martin of Tours St Martin's Church is one of the oldest churches in Worms. This Romanesque church dedicated to St Martin of Tours was a gift of the the Emperor Otto III at the end of the 10th century. The church was rebuilt in the early 13th century. Largely destroyed in a fire in 1689 the church was rebuilt in the Baroque style. The church was badly damaged during WWII bombing raids. Peter Fredrich Wallreuther (1712-1794) was the canon and dean of St Martin from 1776 until his death in 1794. He was buried there. See Peter Fredrich Wallreuther and Wallreuther While a Roman Officer under the Emperor Julian Apostata, St. Martin of Tours was imprisoned in Worms because as a Christian he no longer wanted to fight against the Germanic tribes. St. Martin's church was built on the site of the prison. Joachim Specht suggests Feast of St Martin (Martinmas) and Martinsstift (Worms) for more information on St. Martin and his church in Worms.
| |
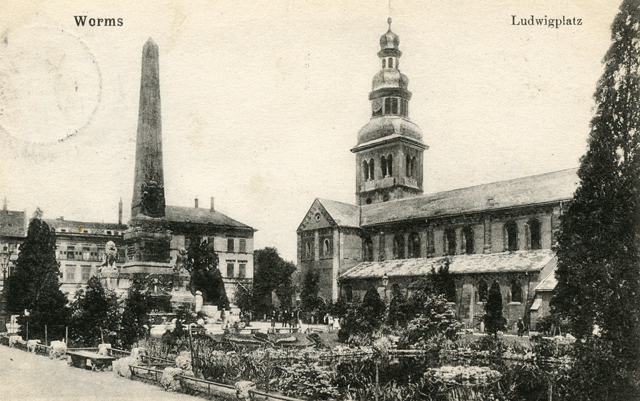
| |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck
Worms
Ludwigplatz Martinskirche, the church of St. Martin of Tours. Peter Fredrich Wallreuther (1712-1794) is buried in this church. Wandgrab des Priesters Wallreuther von 1786 in der Vorhalle. Ein vor einem Obelisken ruhendes schlafendes Kind hält das Wappen, welches durch ein goldenes mit schwarzen Sternen versehenes Band in zwei Felder geteilt wird und auf dem oberen einen Vogel in blau, auf dem unteren drei Rosen (Tinktur?) zeigt. Unter dem Wappen die Grabschrift. | |
| |
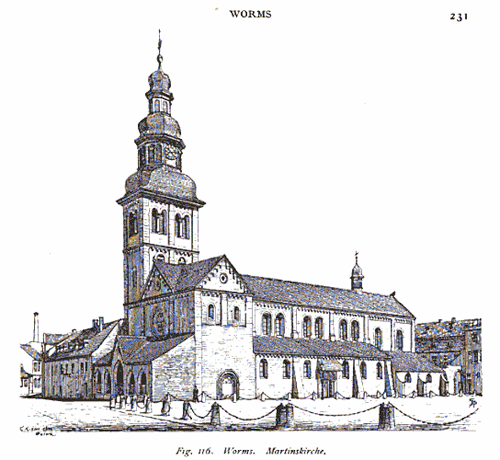
| Google Book, Harvard Library, Kunstdenkmäler im Grossherzogthum Hessen:
Inventarisirung und ..., 1877
Worms Martinskirche [Church of St. Martin]
| |
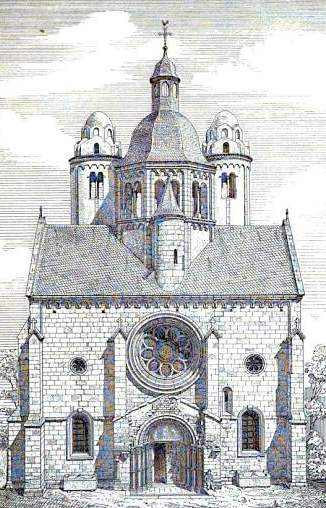
| Paulskirche, St Pauls Chruch The history of St Paul's church is quite similar to that of St. Martin. Founded in 1002 it was rebuilt in the 13th century in the Romanesque style. North of the church there was a Gothic cloister. The church was destroyed in he Palatine war of Succession in 1689. It was rebuilt in the Baroque style. In 1797 the monastery was abolished by the French. The church served as a warehouse and later as a museum. It too was badly damaged in WWII. It is now the church of the Dominican monastery of Worms. Philipp Franz Ignacio Wallreuther (1751-1811) was a canon at St. Paul's in Worms. See Dominikaner an St. Paulus and Wallreuther | |

| |
| Collection of Maggie Land Blanck, 2013
Worms - Eglise S. Paul de Worms bâtie en 1016 [Church of St. Paul in Worms built in 1016]
| |
| |
| Google Book, Harvard Library, Kunstdenkmäler im Grossherzogthum Hessen:
Inventarisirung und ..., 1877
Worms Pauluskirche
| |
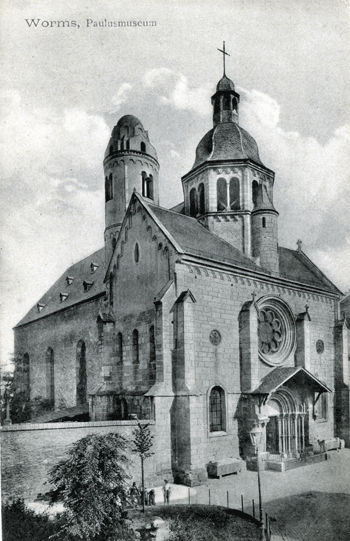
| |
|
Postcard collection of Maggie Land
Blanck, September 2011 Worms Pauluskirche
| |
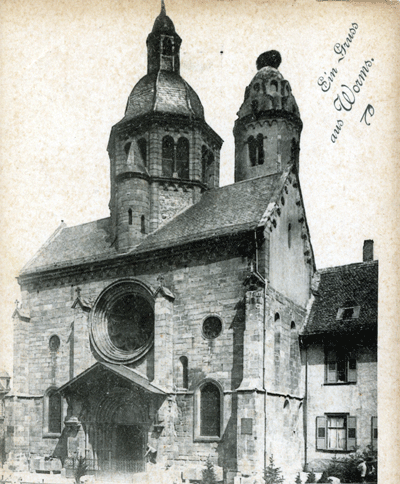
|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011
Worms Pauluskirche
|

| |
| Google Book,
Fest-Gabe zur Eröffnung des Paulus-Museums zu Worms, 9. October 1881. Die St ... By Friedrich Karl W. Schneider
Worms St Paulus Kirch [Church of St. Paul]. Philip Franz Ignacio Wallreuther born 1751 and graduated Heidelberg 1769 was cantor of this church.
| |
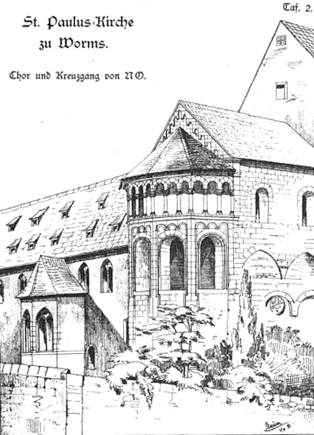
| |
| Google Book,
Fest-Gabe zur Eröffnung des Paulus-Museums zu Worms, 9. October 1881. Die St ... By Friedrich Karl W. Schneider
Worms St Paulus Kirch [Church of St. Paul]. Choir and cloister. | |

| |
| Google Book,
Fest-Gabe zur Eröffnung des Paulus-Museums zu Worms, 9. October 1881. Die St ... By Friedrich Karl
W. Schneider
Worms St Paulus Kirch [Church of St. Paul]. | |
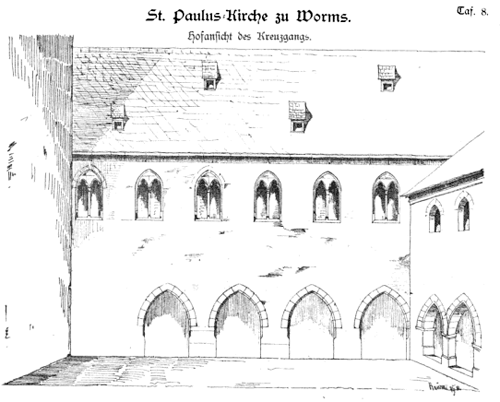
| |
| Google Book,
Fest-Gabe zur Eröffnung des Paulus-Museums zu Worms, 9. October 1881. Die St ... By Friedrich Karl W. Schneider
Worms St Paulus Kirch [Church of St. Paul]. | |

| |
| Google Book - Kunstdenkmäler im Grossherzogthum Hessen: Inventarisirung und beschreibende ... 1887
Worms Pauluskirche [Church of St. Paul]
| |
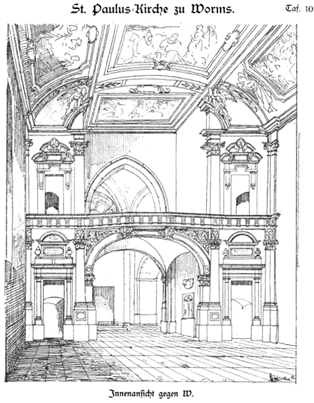
| |
| Google Book, Kunstdenkmäler im Grossherzogthum Hessen: Inventarisirung und beschreibende ... 1887
Church of St. Paul, Worms | |
| Andreaskirche
| |

| Labeled on back
Photogr. Westenfelder, Worms. Not postedSt Andrew's Church cloister which dates to the 13th century is now part of the Museum der Stadt Worms. |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck | |
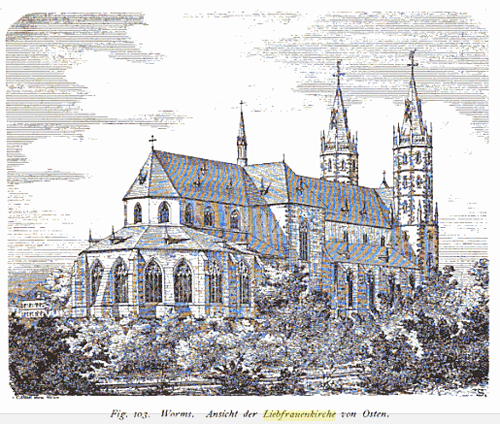
| Liebfraurenkirche
| |

|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck Liebfrauenkirche — 14th and 15th century late Gothic church. The vineyards surrounding the church are the original home of the famous white wine, Liebfrauenmilch [Beloved Lady's Milk]
|
| |
| Google Book,
Kunstdenkmäler im Grossherzogthum Hessen: Inventarisirung und
beschreibende ..., 1877
Liebfrauenkirche Johann Anton Wallreuther (1672-1734) Auxiliary Bishop of Worms 1731-24 is buried in the Liebfraukirche. He was canon at Liebfruenkirche from about 1705 to 1711. He was originally buried in the Church of St. John but when that church was demolished in 1812 his tomb was moved to Liebfrauenkirche. Information from Joachim Specht, 2011. | |

| |
| Google Book,
Kunstdenkmäler im Grossherzogthum Hessen: Inventarisirung und
beschreibende ..., 1877
Liebfrauenkirche Westportal
| |

| |
| Google Book,
Kunstdenkmäler im Grossherzogthum Hessen: Inventarisirung und
beschreibende ..., 1877
Liebfrauenkirche Südportal
| |
| Ev. Luthergemeinde Worms The Lutherkirche was constructed 1910-1912. IEN FESTE BURG IST UNSER GOTT ("A Mighty Fortress is our God" is a hymn written by Martin Luther) |
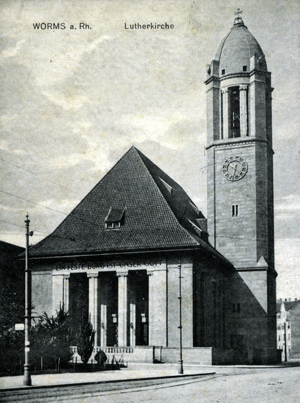
| |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011
| |
| Ancient Walls The Ancient Walls of Worms date to medieval times. When Worms was at the height of its power and prestige in the fifteenth century the city walls, pierced by 12 gates, surrounded five castles, 30 palaces, 12 monasteries, five abbeys and 50 churches, as well as the residence of the Emperor and the Bishop, and the great romanesque cathedral. | |

|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck
The Raschitor was the entrance to the Jewish area of Worms. |

| |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck Worms Am Rhein Alte Stadtmauer und Lutherpfortchen [ancient city wall with Lutherpförtchen]
| |

| |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011 Lutherpförtchen | |
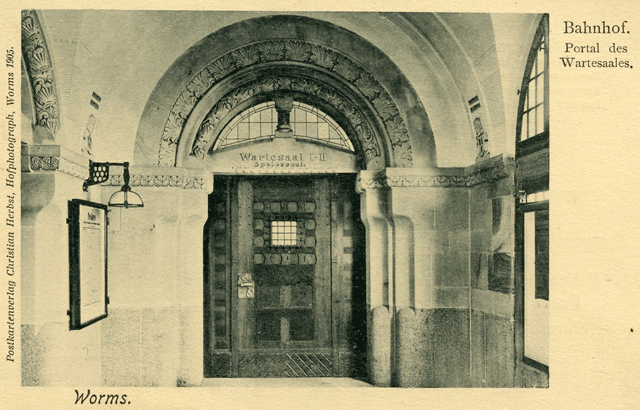
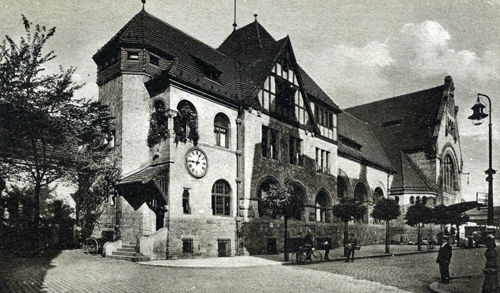
| Bahnhof A train line between Mainz and Worms opened in the summer of 1853.The following images are of the third station in Worms which was opened in 1904. The station was badly damaged during WWII. | |
|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck
Worms
Bahnhof - Portal des Wartesaales 1905 |

| |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011 Worms A. Rhein Hauptbahnhof | |
| |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011 Worms A. Rhein Bahnhof, 1917 | |
| Kammererstraße
| |

|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011 Worms A. Rhein Kammererstraße, 1919 |
| Festspielhaus
| |

|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011
Festspielhaus, Worms a. Rh. Festival Hall Theater, built 1888-89. See CARTHALIA - Worms: Spiel- und Festhaus (old)
|
| Lutherplatz This monument to Luther was built in 1868.
| |

|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011 Lutherplatz 1919 |
| Hafen
| |

|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck, September 2011 Worms Hafen [Harbor] |
| The Rhine
| |
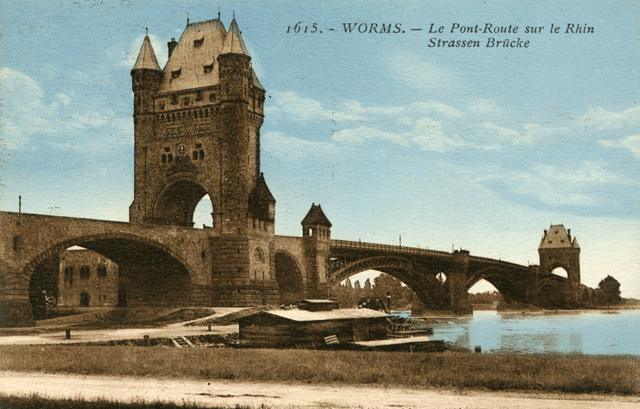
|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck Worms The bridge over the Rhine Another postcard with a very similar view labels this "Ernst Ludwigbrucke". The first permanent bridge across the Rhine near at worms was build in 1900. It was called the Ernst Ludwig bride and was destroyed during WWII. The Nebelungen bridge was built between 1951 and 1953. |
 |
|
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck | |
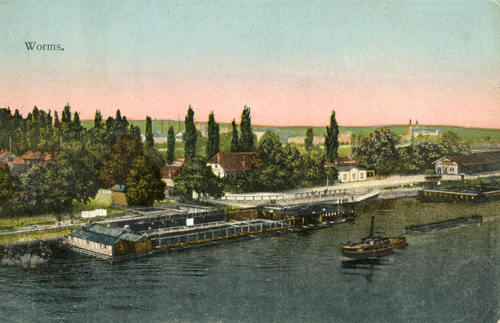
| Worms, The Rhine River |
| Postcard collection of Maggie Land Blanck Worms is located in the Rhineland Palatinate of the Rhine River. | |
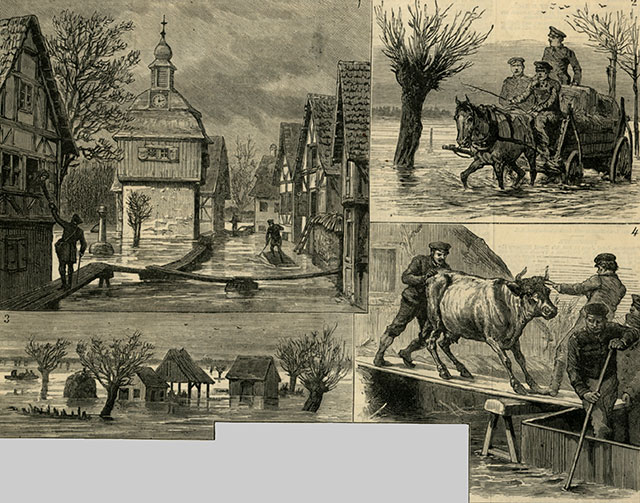

| |
| Collection of Maggie Land Blanck, 2013
Illustrated London News January 20, 1883 - INUNDATIONS OF THE RHINE IN HESSE-DARMSTADT 1. The main street of Dornberg, 2. Taking provisions to flooded villages 3. Flooded fields of Gross Ge an, 4. Saving cattle from the flood
| |
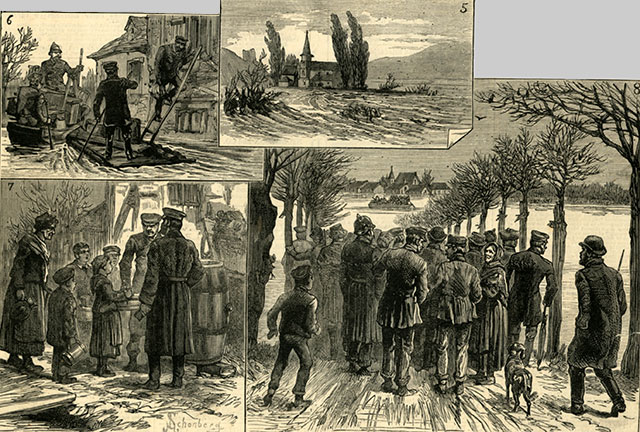

| |
| Collection of Maggie Land Blanck, 2013
Illustrated London News January 20, 1883 - INUNDATIONS OF THE RHINE IN HESSE-DARMSTADT 5. Clemens Chapel on the Rhine, 6. Moving furniture at Wallerstadten, 7. Distributing drinking waster and provisions among the poor of Dornberg, 8. Waiting the arrival of fugitives from the flooded villages. The Rhine between Basil and Bingen often flooded: Extreme floods occurred 1758, 1784, 1813, 1876 and 1882/1883). Floods On The Continent - The Rhine Valley, so familiar to English tourists, has been desolated by floods. In November there was much damage done by the Rhine and its swollen effluents, but nothing in comparison to what was done at the close of the year. The uplands were thickly covered with snow, the fall of which was followed by some days of very mild weather and heavy rain, and the rivers which feed the Rhine rose not only inches but feet in an hour or two, and from the Lake of Constance to the Dutch frontier, miles upon miles of the country were under water. Embankments were washed away, and whole villages destroyed. Just below the town of Mannheim the valley was like a wild, turbulent sea, and over an immense area nothing was to be seen above the waste of waters, save here and there a tall tree top or the spire of a church. Along the course of the Danube it has been much the same, though perhaps not quite so bad as along the Rhine. Thousands of people in both valleys are houseless and destitute, having lost all they had, and suffered, in addition to this, the loss of many of their kinsfolk."Near Worms, 12 villages nearly destroyed, 10,000 people destitute." (Reports and Transactions By Cardiff Naturalists' Society) At Worms the Hammel dyke on the Rhine burst and flooded the lower part of the town. 500 to 600 houses in Worms were said to have been destroyed by the flood of 1883. 10,000 people near Worms were said to have become homeless. Peter Goehle from Herrnshiem, a village outside of Worms, had been in New York City ten years when his flood occurred. His father, Franz, was still alive in 1883. | |
| WORMS Kreisstadt im Großherzogtum Hessen, Provinz Rheinhessen, IMAGES OF WORMS |
|
|
|
Wallreuther Kieser Peter Goehle Herrnsheim Goehles in Herrnsheim |
|
RETURN TO TOP OF PAGE
|
| If you have any suggestions, corrections, information, copies of documents, or photos that you would like to share with this page, please contact me at maggie@maggieblanck.com |
| ©Maggie Land Blanck - Page created 2008 - Latest update, June 2016 |